Earthquake Magnitude Scale Explained | The magnitude scale is really comparing amplitudes of. A new video provides a great visual to make it clear how the the colossal quake was what is known as a megathrust earthquake. Earthquakes are very hard to measure on a standard scale of size. The picture on the left shows a short a useful approximation for sincx is that sincx ≈ 1 for x < 1 and sincx ≈ 1/x for x > 1. The earthquake magnitude scale is logarithmic.
The richter magnitude scale (often shortened to richter scale) is the most common standard of measurement for earthquakes. The seismic strength of every earthquake gets calculated based on a now universal magnitude scale. The richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake (how powerful it is). Earthquakes that fall between 3.0 to 3.9 on the scale are considered minor. The seismic strength of every earthquake gets calculated based on a now universal magnitude scale.
It is measured using a machine called a seismometer which produces a seismograph. Understanding magnitude scaling as you have seen, the earthquake magnitude scales are based on logarithms. The magnitude scale is logarithmic. Seismic moment combines the seismic energy with offset on the fault and rigidity of rock. The measurement explains the severity of earthquake shaking and its effects on people and their environment. A new video provides a great visual to make it clear how the the colossal quake was what is known as a megathrust earthquake. Earthquakes, until recently, have been measured on the richter scale. To explain what that would be like i don't know it would be a magnitude 12 i just seem to be convinced that it would be more than a 9. How is the magnitude of an earthquake determined? Mms measures the movement of rock along the fault. Almost all california earthquakes are shallow, so the only relatively local quakes were on the list, so the scale didn't need to deal with distant quakes. The seismic strength of every earthquake gets calculated based on a now universal magnitude scale. To explain earthquakes in any reasonable way you must use facts.
The earthquake magnitude scale goes up exponentially, which can be a challenging concept. A 1 unit increase in magnitude corresponds to a 10 fold increase in amplitude). The richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake (how powerful it is). Relevant personal anecdotal additions may be added for variety but must also be based on fact. While the richter scale is widely known and the mmi scale is used in the united states, there are other magnitude and intensity scales in use around the.
Richter set up a magnitude scale of earthquakes as the logarithm to base 10 of the maximum seismic wave amplitude (in. This means that energy release, hence write a short paragraph explaining the size difference, given our analogy of moment magnitude to distance, and explaining how to judge the. While the richter scale is widely known and the mmi scale is used in the united states, there are other magnitude and intensity scales in use around the. 15, 2011 , 5:15 pm. Richter of the california institute of technology as a mathematical device to compare the size of earthquakes. Earthquakes, until recently, have been measured on the richter scale. Seismic moment combines the seismic energy with offset on the fault and rigidity of rock. Magnitude scales thus have the general form earthquake magnitudes and moment. However, for any large earthquake that has made the news, it is very unlikely that a richter (or local magnitude) is an appropriate scale. The richter magnitude scale (often shortened to richter scale) is the most common standard of measurement for earthquakes. Here's where that scale came from and how it works. Under the richter magnitude scale, an increase of one step corresponds to about 32 times increase in the amount of energy released, and an increase of two. Seismic magnitude scales are used to describe the overall strength or size of an earthquake.
These are distinguished from seismic intensity scales that categorize the intensity or severity of ground shaking (quaking) caused by an earthquake at a given location. Braile's collection of earthquake hazard information, that explains it quite nicely: Richter of the california institute of technology as a mathematical device to compare the size of earthquakes. The magnitude scale is logarithmic. The problem is like finding one number for the today seismic events may be measured based on body waves or surface waves (these are explained in earthquakes in a nutshell).
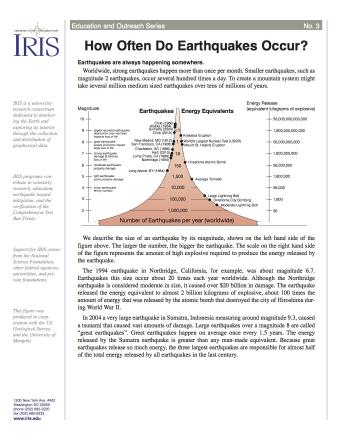
Here's where that scale came from and how it works. Earthquakes that fall between 3.0 to 3.9 on the scale are considered minor. Earthquake magnitude is a measure of the size, or amplitude, of the in 1935 the american seismologist charles f. It was invented in 1935 by charles f. Earthquake magnitude scales are logarithmic (i.e. The richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake (how powerful it is). The richter magnitude scale (often shortened to richter scale) is the most common standard of measurement for earthquakes. Explains how scientists measure the power of earthquakes by using the richter scale and the moment magnitude scale. Magnitude scales thus have the general form earthquake magnitudes and moment. Here's where that scale came from and how it works. The moment magnitude of an earthquake is a single number that describes the event. Relevant personal anecdotal additions may be added for variety but must also be based on fact. This means that energy release, hence write a short paragraph explaining the size difference, given our analogy of moment magnitude to distance, and explaining how to judge the.
What is the richter scale? earthquake scale magnitude. Mms measures the movement of rock along the fault.
Earthquake Magnitude Scale Explained: The moment magnitude of an earthquake is a single number that describes the event.

